What is trapped water?
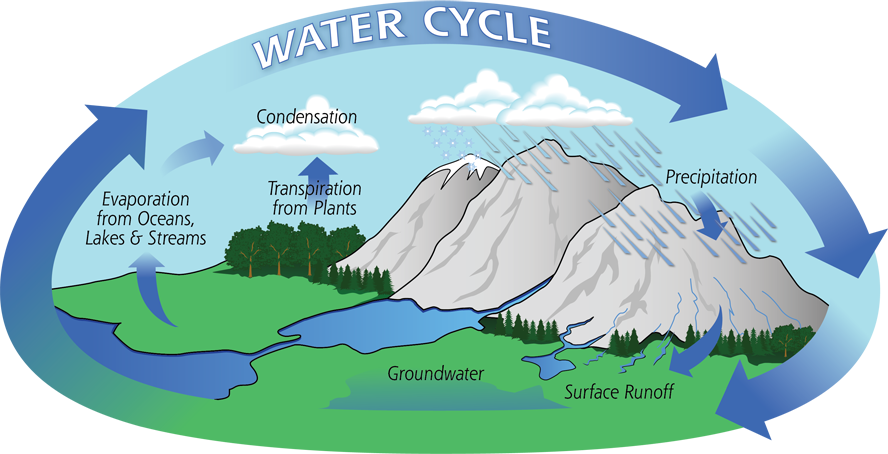
To understand what is trapped water, we need to understand how the water cycle. The water cycle, a fundamental natural process, involves the continuous movement and transformation of water between the atmosphere, land, and oceans. While the intricate dance of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation seems impervious to human influence, even seemingly insignificant factors can play a role. One such factor is the trapped water inside plastic bottles. Though often overlooked, it has subtle yet noteworthy implications for the local water cycle and environmental dynamics which is very important for a better green future.
Why should we care about trapped water?
- Water Sequestration: Trapped water in plastic bottles represents a small but measurable amount of water sequestered from the natural water cycle. Typically found in discarded single-use plastic bottles, this water is denied participation in the intricate cycles of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation that characterize the water cycle.
- Evaporation Disruption: Evaporation, a critical phase of the water cycle, involves the conversion of water from liquid to vapor. When water is trapped in plastic bottles, this natural process is disrupted. The confined water cannot evaporate into the atmosphere, altering local humidity levels and microclimates in the immediate vicinity of the trapped water.
- Microclimatic Effects: Trapped water in plastic bottles may create localized microclimatic effects. The absence of evaporation from these containers can influence temperature and humidity conditions in their immediate surroundings. While the impact is modest, it adds an extra layer to the intricate interplay of environmental factors.
- Ecological Consequences: Local ecosystems can be affected by trapped water in plastic bottles. Flora and fauna relying on natural water sources may face challenges when these sources are disrupted by the presence of confined water. The altered conditions can impact the growth of plants and the habits of local wildlife.
- Potential for Pollution: Trapped water in plastic bottles, when improperly discarded, may contribute to pollution. The stagnant water becomes a breeding ground for bacteria, algae, and mosquitoes, potentially leading to localized contamination. When these bottles end up in water bodies or on the ground, the trapped water, along with contaminants, may enter the broader environment.
- Extended Lifespan in Landfills: Disposed plastic bottles, laden with trapped water, contribute to the longevity of plastic waste in landfills. The added weight from trapped water slows down the decomposition process, extending the time these bottles persist in landfills and adding to the challenges of waste management.
What should we do about it?
While the impact of trapped water in plastic bottles on the water cycle may seem negligible in the grand scheme of global environmental concerns, it underscores the interconnectedness of human activities and natural processes. Responsible waste management, reduction of single-use plastics, and increased awareness of these subtle influences can collectively contribute to mitigating the impacts of trapped water on the local water cycle. In our pursuit of environmental sustainability, even seemingly trivial aspects deserve attention as we strive to maintain the delicate balance of the Earth’s ecosystems.
So next time before you throw away your bottled water or drinks, empty it before throwing! Be part of the team Better Green Future.
If you are interested in reading more about trapped water, you can also read this article.
Woman warns against the dangerous phenomenon that is ‘trapped water’: ‘I’ve never thought about this’
If you like our post, do not forget to subscribe.
We are Better Green Future who fight to ensure own next generation has a future.
